update April 7th 2019: PAAG is now part of the "Pixel Art Historical Society" Wiki at
http://pixelwiki.comun.seupdate Nov. 17th 2018: Porting (plus some additions and edits) this glossary is finished.
update Nov. 9th 2018: I have starting porting this glossary to a proper wiki at
http://paag.dennisbusch.de which will make maintenance and expansion much easier. So the glossary in the first post of this thread will not be updated anymore. I will still watch this thread for suggestions on terms that should be included in the glossary.
short title: Pixels And Art Glossarylong title: 'a non-exhaustive Pixels And Art Glossary, descriptive in nature, compiled from some of the elements observed in what is vaguely known as "Pixel Art", from historical technological evolution of computer graphics(~1970-2000) and from thoughts developed by the major Pixel Art communities on the internet (199x and up)'
scope and intention:This is NOT an attempt to create and provide a formal definition of "Pixel Art" nor an attempt at providing a ruleset on good and bad practices. It is to be understood as being
purely descriptive. I shall also attempt to keep the final document descriptive and not judgemental, so e.g. something like "Pillow Shading" will be included but there will be nothing in the description which advises for or against doing it (should be self evident to the readers to make the "right" decision from seeing a pillow shaded image without rubbing it in their face).
Most entries already have at least a brief summary and/or links to vast amounts of information on everyones favorite open encyclopedia.
Readers of this thread are encouraged to
throw in Terms which should be included in the Glossary.
Glossary Index
5 P's and 5 C'sAchromatic ColorAliasing & AntialiasingAmigaAnimationAreaAspect RatioAttribute CellsAttribute ClashBandingBitmap & BitdepthBlurBrightness, Lightness & ValueCabinet ProjectionCavalier ProjectionCamera ObscuraCartesian Coordinate SystemCGAClusterColorColor BalanceColor CyclingColor DepthColor Model - HSL/HSV(HSB)Color Model - RGBColor Gradient/Ramp/ShiftColor SchemeColor SpaceCommodore 64CompositionConstructionContourContrastCross SectionDigital Mixing Of ColorDitheringDither-AADrawingEGAElevationFormatClusterForeshorteningGestureGradientGraphic ModeProjectionGIFHistory Of Pixel ArtHueHue ShiftImageIndexed Image/ColorIndex PaintingIsometric ProjectionJPG, JPEGKeyLayerLossy&Lossless CompressionLineRestrictionsLightingLightness (aka Value, aka Tone)Graphics ModeMonochromatic ColorMotion BlurMSXNESNegative SpaceOblique ProjectionOekakiOrthographic ProjectionOutlinePNGPalettePalette EffectPalette StructurePalette SwapPalette Swap - Color CyclingPainting With PixelsParallel ProjectionPerspectivePerspective ProjectionPerceptionPicture PlanePillow ShadingPixelPlanProjection (Graphical)Raster(Aspect) RatioRampResolutionRestrictionsRenderingSaturationSeloutSetSequenceShadeShadingShapeShape BluffingSketchSpriteStyleSVGATall PixelTextureTile & TilesetTintValue & KeyVGAVisual ArtsVideo Game GraphicsVolumeWireframingWide PixelX-axisy-axisz-axisZX Spectrum--- # ---
5 P's and 5 C'sAccording to Andrew Loomis (see his book "Successful Drawing"), in any succesful drawing, attention must be given to five P's and five C's as Loomis calls them. These are (this is a quote from pages 18,19 in that book):
Proportion, the three dimensions
Placement, a position in space
Perspective, relationship of viewpoint to subject
Planes, surface appearance as defined by light and shadow
Pattern, the deliberate arrangement of the tones on the subject
Conception, a rough indication of an idea
Construction, an attempt to establish the forms from life or from basic knowledge
Contour, the limits of forms in space, according to viewpoint
Character, the specific qualities of individual units of your subject in light
Consistency, all the essentials of construction, lighting, and pattern, organized as a unit
--- A ---
Achromatic ColorLiterally a color "without color", which is all shades of gray and black and white.
Practically all colors without a strong perceptual chromaticity are called achromatic.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_scheme#Achromatic_colorshttps://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Achromatic_color&redirect=noAliasing & Antialiasing
further reading:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aliasinghttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/JaggiesAmigahttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/AmigaAnimation
further reading:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/AnimationArea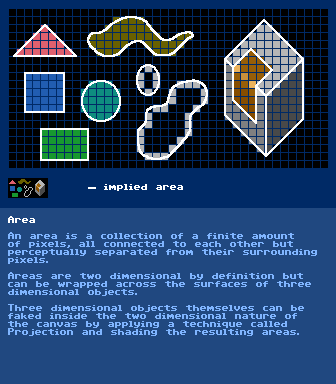
further reading:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/AreaAspect Ratiohttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pixel_aspect_ratiohttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Display_aspect_ratiohttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aspect_ratio_(image)Attribute Cells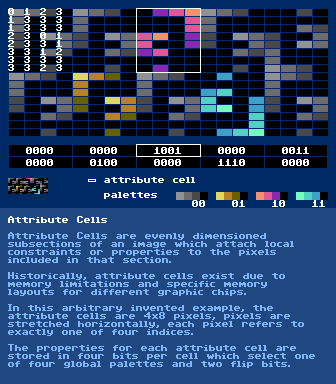
further reading:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ZX_Spectrum_graphic_modeshttp://www.studiostyle.sk/dmagic/gallery/gfxmodes.htmAttribute Clash
further reading:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Attribute_clash--- B ---
Banding
further reading:
Not to be confused with
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Colour_banding which refers to the distinctly visible changes between stripes of colors hugging each other in what was supposed to look like a soft gradient.
Bitmap & Bitdepth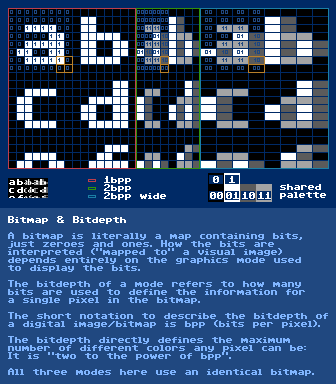
further reading:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bitmaphttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Raster_graphicsBlur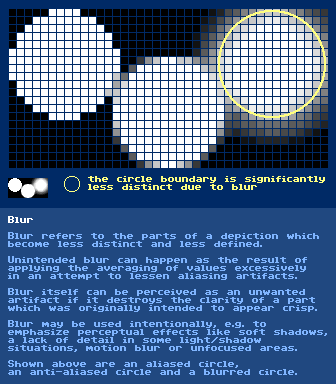
further reading:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Defocus_aberrationhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Motion_blurhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BokehBrightness, Lightness & Value
further reading:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brightnesshttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lightnesshttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HSL_and_HSV (L in HSL is NOT "Lightness As Value" but some arbitrary Brightness)
--- C ---
Cabinet Projection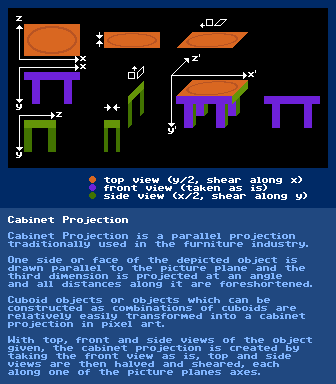
further reading:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oblique_projection#Cabinet_projectionCavalier Projection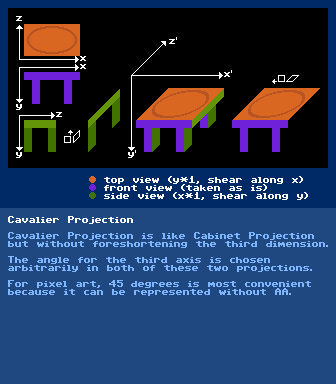
further reading:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oblique_projection#Cavalier_projectionCamera Obscurahttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Camera_obscuraCartesian Coordinate Systemhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cartesian_coordinate_systemCGAhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_Graphics_AdapterCluster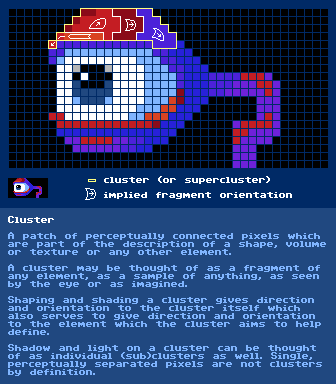
further reading:
http://wayofthepixel.net/index.php?topic=8110.0 - Ramblethread
http://wayofthepixel.net/index.php?topic=15566.0 - 1st Cluster Study Thread
http://wayofthepixel.net/index.php?topic=15018.0 - 2nd Cluster Study Thread
(just search for "cluster" on this board... there are a few more

)
Color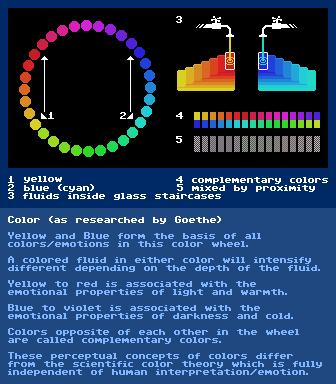
video:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MmhSXTMTtJM "Light Darkness And Colours - A Fascinating Journey Through The Universe Of Colours" 51m15s
further reading:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Theory_of_Colourshttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_theoryhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Complementary_colorshttp://i.imgur.com/vDHMURo.jpg - chronologically ordered set of different color systems
Color Balancehttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_balanceColor Cycling, see
Palette Swap - Color CyclingColor Depthhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_depthColor Model - HSL/HSV(HSB)https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HSL_and_HSVColor Model - RGBhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RGB_color_modelColor Gradient/Ramp/Shift
further reading:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_gradienthttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tints_and_shadeshttp://www.dennisbusch.de/dcgg.php - Dynamic Color Gradient Generator
Color Schemehttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_schemeColor Spacehttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_spaceCommodore 64https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Commodore_64Compositionhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Composition_(visual_arts)Construction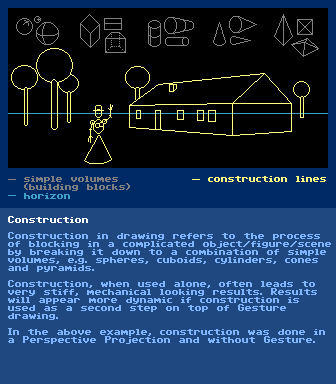
further reading:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Drawing#Form_and_proportionhttps://www.google.com/?q=drawing+fundamentals+constructionContourThe thin fringe (drawn or perceived) between everything that is part of an object and everything that is not part of that object.
ContrastA difference between any two things. Hues can contrast (see complementary colors). Values can contrast. Shapes can contrast (e.g. round shapes contrast pointy shapes). Lines can contrast (horizontals contrast verticals, wavy lines contrast straights). Pretty much any thing has the potential to create a strong perceptual difference between itself and something else.
Cross Sectionhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cross_section_(geometry)--- D ---
Digital Mixing Of ColorIs done by changing the components of a color in a digital color model (such as RGB) or by placing differently colored pixels close to each other (mixing by proximity, called Dithering).
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Additive_colorhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_mixingDitheringDither-AA 
further reading:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ditherhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dither#Digital_photography_and_image_processingDrawinghttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Drawing--- E ---
EGAhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enhanced_Graphics_AdapterElevationhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multiview_orthographic_projection#Elevation--- F ---
FormatFor pixel art, make sure to use any "lossless compression" format. PNG is a good one.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image_file_formatsFragment, see
ClusterForeshorteninghttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Perspective_(graphical)#Foreshortening--- G ---
Gesturehttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gesture_drawinghttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=74HR59yFZ7Y - How to Draw Gesture by Stan Prokopenko
Gradient, regular and irregular, following an outline, following a volume
(pillow shading = gradient hugs an outline/contour instead of wrapping across a surface or following light/shadow logic over a volume)
Graphic Modehttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer_display_standardhttp://www.studiostyle.sk/dmagic/gallery/gfxmodes.htm - some C64 Graphic Modes
Graphical Projection, see
ProjectionGIFhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GIF--- H ---
History Of Pixel Artsee
The History Of Pixel ArtHuehttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HueHue ShiftA Color Shift in which the Hue property of the initial color is shifted to another Hue. Often (arbitrarily) used to render the light and dark parts of shaded volumes with a different Hue in addition to a different Lightness. There are observable phenomena in nature which show shifts in Hue (see also Color) under some lighting conditions.
--- I ---
Imagehttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_imagehttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Raster_graphicsIndexed Image/ColorAn image saved with a limited amount of colors, each color refered to in the raster as the index number at which it occurs in the palette, see also palette.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Indexed_colorIndex PaintingCreating Pixel Art in Indexed Modes, working with Indexed Images while paying attention to
Palette Structure and keeping possible
Palette Effects in mind and at all times keeping control over (if necessary by fixing the results) the pixel level polish of a piece even when using tools that influence more than one pixel at a time.
Historically, "Index Painting" is the natural way to go and think about making Pixel Art as most hardware and digital image editing tools either used Indexed Modes as the default mode or simply did not provide any other modes. The term "Index Painting" was not around then because there simply was nothing else. Today the term seems to be used to set "Pixel Art"(in the sense of Index Painting) apart from other "Pixel Art"(in the sense of Digital Painting and Computer Generated Imagery(e.g. 3D renderings)) and the third kind of "Pixel Art"(the purists "one pixel at a time"- process).
Some advocate placing one pixel at a time as the only "allowed" process to create "Pixel Art"(a term which eludes definition itself) while others advocate whether something is or is not "Pixel Art" can not be defined by processes but only by looking at the results.
The actual term "Index Painting" emerged from the on-going online debate about "pixel purism", processes and results:
http://www.danfessler.com/blog/pixel-purism-process-vs-resultshttp://www.danfessler.com/blog/hd-index-painting-in-photoshopIsometric Projectionhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Isometric_projectionhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Isometric_graphics_in_video_games_and_pixel_artIsometric Pixel Art Cheat Sheet--- J ---
JPG, JPEGThis lossy digital image format is unsuitable to store pixel art because of compression artifacts.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/JPEG--- K ---
Key, see
Value & Key--- L ---
Layerhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Layers_(digital_image_editing)https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2D_computer_graphics#LayersLossy&Lossless Compressionhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image_file_formats#Image_file_compressionLine purpose and functions of a line
todo:
Line Art (emphasize the difference between a painterly sketch here and present line art as a way to define a depiction of something without fully rendering it, also mention variations in line-width effects and point out the perceptual thickness of lines in relation to resolution and shape size of any part of something)
Limitations (see
Restrictions)
Lightinghttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LightingLightness (aka Value, aka Tone)https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lightness--- M ---
Mode, see
Graphics ModeMonochromatic ColorAll tints, tones and shades of equal hue.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_scheme#Monochromatic_colorshttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Monochromatic_colorMotion BlurVisual swooshy action hints or the perceived blur along the path of movement of an object when your camera or eyes can not sample it fast enough to get a crisp image.
MSXhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MSX--- N ---
NEShttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nintendo_Entertainment_SystemNegative SpaceAll space that does not contain anything of the currently observed object.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Negative_space--- O ---
Oblique Projectionhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oblique_projectionOekakihttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OekakiOrthographic Projectionhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Orthographic_projectionOutlineLine around a shape.
--- P ---
PNGhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portable_Network_GraphicsPalettehttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Palette_(computing) (
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Indexed_color )
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_color_paletteshttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_video_game_console_palettesPalette EffectIn Indexed Images/Modes where each pixel in the image refers to a specific color in a sequence of colors(=palette) (instead of holding the full definition of the color in each individual pixel itself), a number of visual effects such as Color Cycling and Color Fading can be achieved by manipulating the palette instead of manipulating the pixels themselves.
This was used a lot on old hardware as manipulating the definition of colors in the palette took much fewer CPU cycles than going through the image and changing the actual pixels themselves.
A simple example for a Palette Effect is just re-defining a color in the palette:
If a thousand pixels in an image referred to color at index five in the palette and index five would hold Green and index twelve would hold Red, all thousand pixels could be changed to Red by changing the color at index five from Green to Red instead of going through the image and looking for every Green pixel and changing the pixel itself to refer to index twelve.
Palette Structure Palette Swap
Palette Swap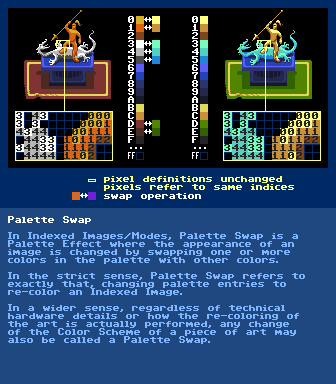
further reading:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Palette_swapPalette Swap - Color Cycling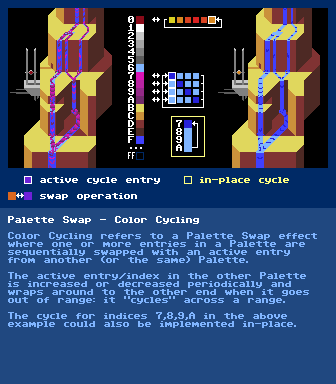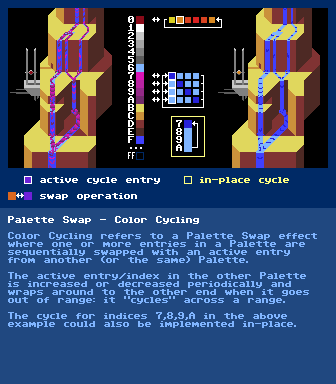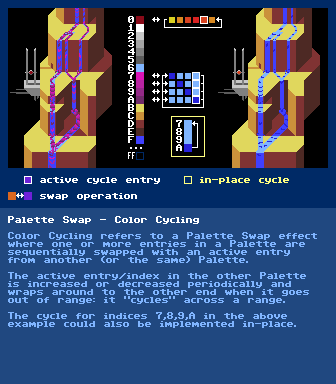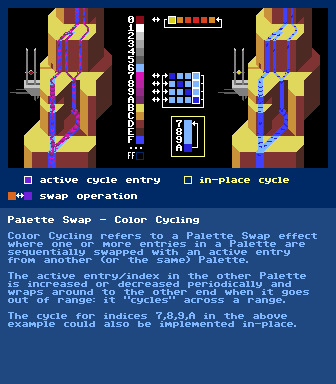
further reading:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_cyclingHTML5 Color Cycling Demo - Art by Mark Ferrari Code by Joseph Huckaby
Painting With PixelsPainting with pixels means to apply blobs/clusters of colored pixels to the raster while thinking like a painter would think with traditional brushes and paint. The difference in (strict) Pixel Art is that the newly placed pixels do not blend or mix in any way with the pixels which are already there on the raster but instead fully replace them (unlike paint which mixes with the paint already on the canvas). Most Pixel Art editing software still has a multitude of painting or brush modes and layer effects though which can still cause a placed blob of pixels to blend/mix with the pixels that are already there.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PaintingParallel Projection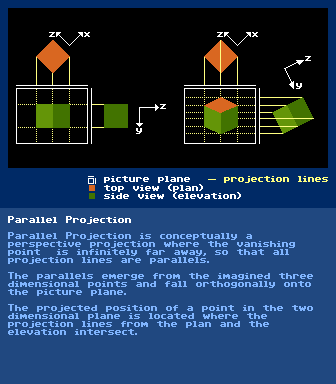
further reading:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parallel_projectionPerspectivehttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Perspective_(graphical)todo: (horizon, vanishing points, planes, measuring points, camera height and angle)
Perspective Projection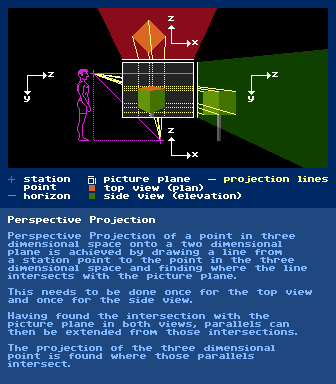
further reading:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Perspective_(graphical)Perceptionhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PerceptionPicture Planehttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Picture_planePillow Shading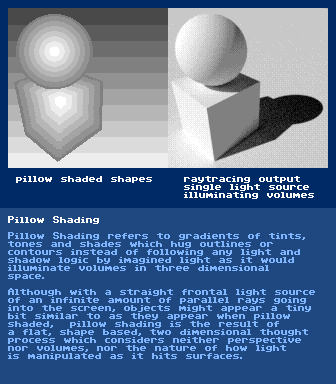 Pixel
Pixel, an element in a digital raster image
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PixelPlanfurther reading:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plan_(drawing)Projection (Graphical)todo: overview image with different projections
further reading:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graphical_projectionhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Floor_planhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multiview_orthographic_projection--- Q ---
--- R ---
Rasterhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Raster_graphicsRatio, see
Aspect RatioRamp (todo: linear, non-linear, refer also to intersection between ramps, talk about value, hue and saturation here as well)
Resolutionhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Display_resolutionhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image_resolutionRestrictionsRestrictions are arbitrarily chosen or real (by hardware limits) limitations imposed upon a work of (pixel) art. The limitations include figures on resolution (horizontal and vertical dimensions of the piece in number of pixels), number of colors which apply globally to the whole image and sometimes additional local restrictions per Attribute Cell.
RenderingThe process of applying value, color and texture to an imagined or wireframed structure in order to arrive at the final depiction of something.
--- S ---
SaturationThe perceived intensity of a specific color(hue).
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ColorfulnessSelouttodo: selective outlining
SetAn un-ordered collection of things: e.g. { Banana, Cherry, Pineapple, Motor Oil }
SequenceAn ordered collection of things, so that each thing in the collection can be referred to explicitly by its index(the 1st element often gets assigned to index 0): e.g. { 0: hamster, 1: gasoline, 2: torch, 3: book of sinister implications }
Shadehttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tints_and_shadesShadingThe process of applying different tints, tones and shades upon volumes in accordance with one or more real or imagined lightsources which illuminate those volumes. The goal of shading is to create an illusion of three-dimensionality on a two-dimensional surface(the canvas or raster).
ShapeA shape is a two dimensional entity. Cutting through a volume with a plane reveals a shape along the cut (see also Cross Section).
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ShapeShape BluffingShape Bluffing means to add abstract detail instead of rendering any specific texture onto a surface. Shapes themselves are two dimensional but the abstract detail added by "Shape"-Bluffing often appears to be three dimensional or aims to add a three-dimensional appearance to the surface/volume over which it is spread.
further reading:
http://pixeljoint.com/pixelart/30531.htmSketch A deliberately rough representation of anything, intended as a base for further work or just to capture a thought/idea or to explore different angles and details of a subject in preparation for a polished work or design. Synonymous with doodle.
Spritehttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sprite_(computer_graphics)StyleA usually limited set of specific ways to depict something, used consistently to achieve a unified look&feel across several elements of a larger collection of pieces.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Style_(visual_arts)SVGAhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Super_video_graphics_array--- T ---
Tall PixelPixel with an Aspect Ratio of 1:2 or any pixel which is taller than it is wide.
Texturehttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Texture_(visual_arts)https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Texture_mappingTile & Tilesethttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tile-based_video_gamehttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tile_enginehttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tiled_renderingTinthttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tints_and_shadesTone, see
Value--- U ---
--- V ---
Value &
Key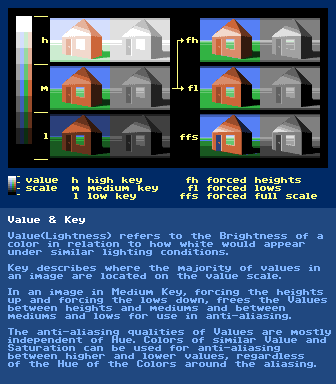
see also
Brightness, Lightness & ValueVGAhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Video_Graphics_ArrayVisual Artshttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Outline_of_the_visual_artsVideo Game Graphicshttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Video_game_graphicsVolumeA three-dimensional body in a three dimensional cartesian coordinate system (e.g. sphere, cuboid, cone, cylinder, pyramid). To get a strong illusion of volumes on a two dimensional surface, it is desirable to employ a suitable projection in addition to shading the volumes consistently according to imagined lightsources and utilizing texture to emphasize surface curvature.
--- W ---
WireframingA quick way to define Volumes first in sketches and in construction without having to fully render them. Also useful to draw the invisible sides of objects to find correct placement and proportion of things which are partially covered by other things.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wire-frame_modelWide PixelPixel with an Aspect Ratio of 2:1 or any pixel that is wider than it is tall.
--- X ---
X-axisThe first dimension in a Cartesian Coordinate System.
--- Y ---
y-axisThe second dimension in a Cartesian Coordinate System.
--- Z ---
z-axisThe third dimension in a Cartesian Coordinate System.
ZX Spectrumhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ZX_Spectrum