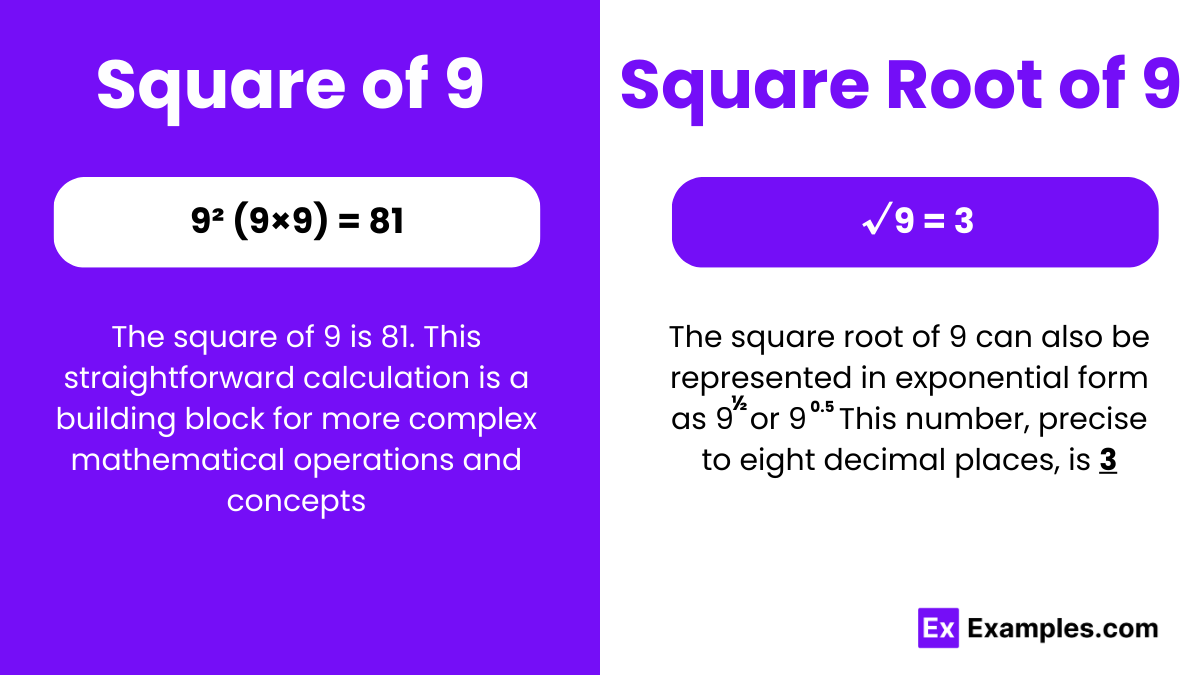
You’re probably here because you need a quick answer for a homework assignment or you're just settling a random debate. The short answer is 3. But honestly, there is so much more to it than that. When we talk about the square root of 9, most people just think of the number three and move on with their lives. But if you're into coding, engineering, or even just high-level logic, that "3" is only half the story.
Math is weird like that. It feels solid until you start poking at the edges.
What the Square Root of 9 Actually Means
At its most basic level, finding a square root is like playing a matching game in reverse. You’re looking for a number that, when multiplied by itself, gives you the original value. So, for the square root of 9, we ask: What number times itself equals 9?
$x^2 = 9$
The most obvious answer is 3. Since $3 \times 3 = 9$, we call 3 the principal square root. It’s the one your calculator shows you when you hit the radical symbol button ($\sqrt{9}$). It’s clean. It’s easy. It’s what we use when we’re measuring the side of a square floor that has an area of 9 square meters. You can’t have a floor that is negative 3 meters long, right? That wouldn't even make sense in the physical world.
But here is where things get a little bit spicy.
In the world of pure mathematics, there’s a second answer. Negative 3. Because $(-3) \times (-3)$ also equals 9. In algebra, this matters a lot. If you’re solving a quadratic equation, ignoring that negative 3 can literally break your entire proof. We usually write this as $\pm 3$ to cover all our bases.
Why 9 is a "Perfect" Number (Literally)
In math speak, 9 is what we call a perfect square.
This isn't just a fancy compliment. A perfect square is an integer that is the square of another integer. Think of it like a club. 1 is in the club ($1 \times 1$). 4 is in the club ($2 \times 2$). 9 is a VIP member because $3 \times 3$ lands exactly on it without any messy decimals or repeating numbers.
Compare that to the square root of 8. That’s roughly 2.828427... and it goes on forever. It’s messy. It’s irrational. 9 is different. It’s stable. Because of this stability, the square root of 9 shows up everywhere in construction and design. If you see a grid or a pattern that feels "right" to the human eye, it’s often because it’s based on these perfect square ratios.
The Geometry of Three
Think about a square. If that square has an area of 9 units, its sides are exactly 3 units long. This sounds simple, but it’s the foundation of how we understand space. In ancient Greece, mathematicians like Pythagoras weren't just looking at numbers on a page; they were looking at pebbles in the sand.
To them, the square root of 9 was a physical reality. You could literally arrange nine pebbles into a perfect 3-by-3 square. If you had 8 pebbles, you couldn't do it. If you had 10, you had one left over. That perfection is why the number 9 held such mystical significance in ancient cultures. It was the end of the single-digit numbers and a gateway to a new level of complexity.
Common Mistakes People Make with Radicals
People mess this up all the time. One of the biggest pitfalls is confusing "square root" with "dividing by two." I’ve seen smart people look at the square root of 9 and instinctively say 4.5. It happens! Our brains are wired for addition and division because we use them every day at the grocery store. Squaring is exponential growth. It’s a different beast.
Another mistake? Forgetting the negative root in algebraic contexts. If you are a student or someone working in a field like physics, forgetting that $x$ could be -3 will lead to "phantom" errors in your data. In electricity, specifically alternating current (AC) theory, these signs determine the direction of flow or phase shifts.
Real-World Applications You Actually Use
You might think you’ll never use the square root of 9 outside of a classroom, but it’s working behind the scenes in your pocket right now.
- Image Compression: When your phone saves a photo as a JPEG, it uses complex math called Discrete Cosine Transforms. This involves breaking the image into blocks (often 8x8 or 9x9) and calculating spatial frequencies using square roots.
- Gaming Engines: If you play games like Fortnite or Call of Duty, the engine is constantly calculating distances between players. To find the distance between two points ($x, y$), the game uses the Pythagorean theorem: $\sqrt{x^2 + y^2}$. If the sum of those squares happens to be 9, the game knows you are exactly 3 units away.
- Architecture: Standardized tiling and structural supports often rely on perfect squares to ensure weight is distributed evenly. A 3x3 support grid is one of the most stable configurations for small-scale platforms.
Taking it Further: The Cube Root
If you’re feeling brave, look at the cube root. The square root of 9 is 3. But the cube root of 9 is something else entirely. It’s about 2.08. This is because $2.08 \times 2.08 \times 2.08$ gets you close to 9.
Why does this matter? Because it shows how quickly numbers scale. Moving from a 2D square (square root) to a 3D cube (cube root) changes the fundamental "base" of the number. Understanding that the square root of 9 is a clean 3 helps you realize how "special" the number 9 is compared to almost any other number around it.
👉 See also: PnP Meaning: Why It’s Not Just a Simple Tech Acronym
Your Next Steps to Mastery
Knowing that the square root of 9 is 3 (and sometimes -3) is just the start. If you want to actually use this knowledge, try these steps:
- Memorize the first 12 perfect squares. It sounds boring, but knowing that 144's root is 12 or 81's root is 9 makes you infinitely faster at mental math and estimation.
- Practice the "Plus-Minus" habit. Every time you solve for a square root in an equation, write $\pm$ before the number. It trains your brain to see the full picture, not just the "easy" answer.
- Check out the Pythagorean Theorem. Look at a right-angled triangle. If the two short sides are 1.8 and 2.4, the long side is the square root of $(1.8^2 + 2.4^2)$. Guess what? That equals the square root of 9. The answer is 3. This 3-4-5 triangle rule is used by carpenters every single day to make sure walls are square.
Math isn't just a set of rules; it's a toolset. And 3 is one of the most versatile tools you've got.