Math isn't always about clean answers. Most of us grew up thinking numbers were supposed to fit into nice, tidy boxes, but the square root of 37 is a perfect example of how messy—and fascinating—the mathematical world actually is. If you're looking for a quick answer, it's roughly 6.08276. But honestly, that tiny decimal is just the tip of a very deep iceberg that stretches into geometry, computer science, and the very nature of infinity.
It's a prime number. 37 doesn't play nice. It doesn't have factors other than one and itself, which makes its square root an irrational number that never ends and never repeats. You can't write it as a fraction. It just goes on forever, like a digital fingerprint of the universe’s complexity.
The Basic Math: Finding the Square Root of 37
When we talk about the square root of 37, we’re basically asking: "What number, when multiplied by itself, gives us 37?"
Since $6^2 = 36$ and $7^2 = 49$, we know right away that the answer has to be just a hair over 6. It’s remarkably close to a perfect square, which makes it a favorite for teachers who want to test if students actually understand estimation or if they're just guessing.
Newton’s Method: The Way Computers Actually Do It
How does your calculator get such a precise answer so fast? It doesn't "know" the answer. It uses something called the Newton-Raphson method. This is an iterative process that closes in on the truth by making an educated guess and then refining it over and over.
If we want to find $x = \sqrt{37}$, we can use the formula:
$$x_{n+1} = \frac{1}{2} \left(x_n + \frac{S}{x_n}\right)$$
Where $S$ is 37. If we start with a guess of 6, the math looks like this:
$$x_1 = \frac{1}{2} \left(6 + \frac{37}{6}\right) = \frac{1}{2} (6 + 6.1666) = 6.0833$$
One iteration. That's all it takes to get incredibly close to the actual value of 6.08276253. It's a testament to how elegant calculus can be when applied to simple arithmetic.
Why 37 Matters in Number Theory
The number 37 itself is a "star number." In geometry, this means 37 points can be arranged to form a centered hexagon, which looks like a star. This isn't just a fun visual trick. It relates to how we understand space and tiling.
👉 See also: Metallic Bonds and Properties of Metals: Why Your Car Doesn’t Shatter When You Hit a Pothole
When you take the square root of a number like 37, you're stepping into the realm of algebraic integers. Specifically, the square root of 37 is linked to the study of real quadratic fields. In the field $\mathbb{Q}(\sqrt{37})$, something very strange happens. Unlike many other similar fields, this one has a "class number" of 1.
In plain English? It means that in this specific mathematical playground, unique factorization still works. This is a big deal for number theorists like those at the American Mathematical Society who spend their lives looking at why certain numbers behave like "normal" integers and others don't.
The Continued Fraction of √37
If you want to see the real beauty of this number, you have to look at its continued fraction. Most irrational numbers have continued fractions that look like a chaotic mess of random digits.
Not 37.
The continued fraction for the square root of 37 is $[6; 12, 12, 12, \dots]$. It’s incredibly rhythmic. This happens because 37 is in the form of $n^2 + 1$. Whenever you take the square root of a number that is exactly one more than a perfect square, the continued fraction follows this specific, predictable pattern. It's one of those rare moments where the chaos of irrationality reveals a hidden structure.
🔗 Read more: Is the Nvidia RTX 3070 Still Worth It in 2026? What Most People Get Wrong
Real-World Applications (Yes, They Exist)
You might think, "When am I ever going to need to know the square root of 37 in real life?"
Fair point.
But if you are a machinist or a carpenter working on a diagonal brace for a rectangular frame that is 6 feet by 1 foot, the hypotenuse of that triangle is exactly $\sqrt{37}$ feet. In high-precision engineering, "roughly 6.08" isn't good enough. If you're building a bridge or a part for a jet engine, that difference between 6.08 and 6.0827 can be the difference between a perfect fit and a mechanical failure.
In the world of technology and signal processing, these "non-clean" square roots are used in algorithms that compress data or encrypt messages. The irrational nature of the number makes it a great candidate for generating pseudo-randomness.
Common Misconceptions About Root 37
People often think that because 37 is a prime number, its square root must be "more" irrational than something like the square root of 8. That's not really how math works. A number is either rational or irrational; there’s no middle ground.
💡 You might also like: How to edit home address on iPhone so Maps actually knows where you live
Another mistake is rounding too early. If you're using the square root of 37 in a multi-step calculation, rounding to 6.1 at the start will throw your final answer off significantly. Always keep the radical form ($\sqrt{37}$) as long as possible before hitting that decimal button on your calculator.
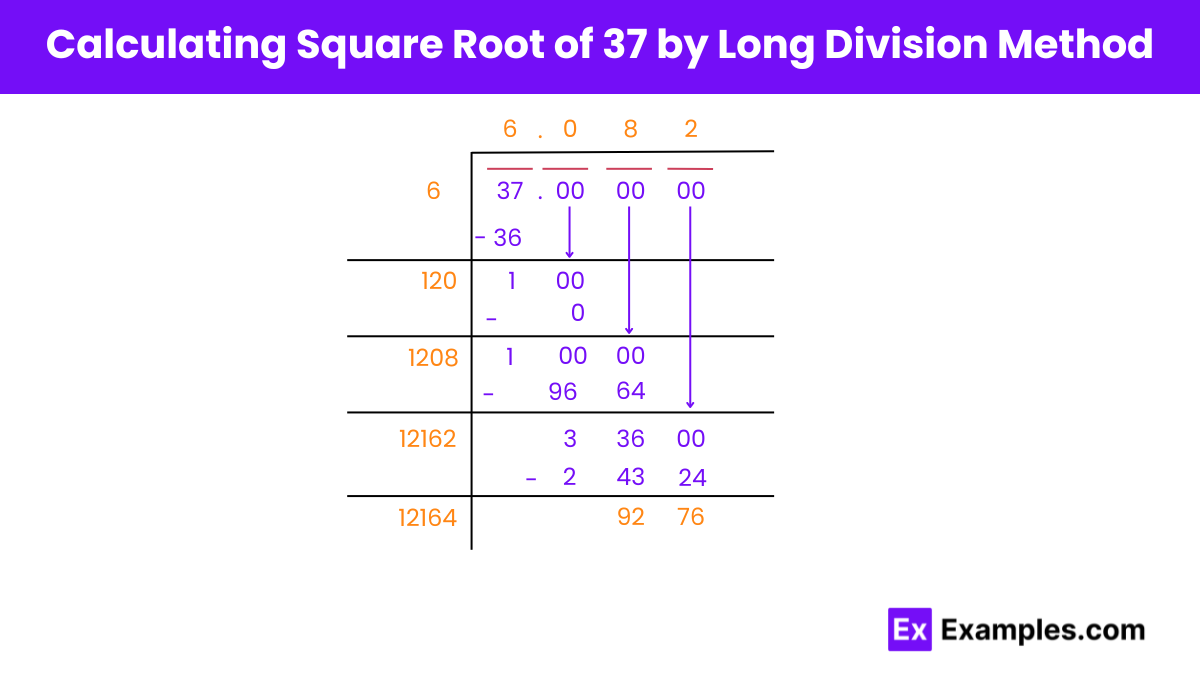
How to Calculate It Manually (The Long Division Way)
Before we had iPhones, people used a method that looks a lot like long division to find square roots. It’s a bit tedious, but it’s a great way to understand what's happening under the hood.
- Group the digits in pairs starting from the decimal point (37. 00 00 00).
- Find the largest square less than 37 (which is 36, from $6 \times 6$).
- Subtract 36 from 37 to get 1, then bring down the first pair of zeros.
- Double your current answer (6) to get 12.
- Find a digit "x" such that $12x \times x$ is less than or equal to 100.
- In this case, even $121 \times 1$ is 121, which is too big for 100. So the next digit is 0.
This is why the decimal starts 6.0... and then moves into the 8. It’s a rhythmic, manual process that makes you appreciate the processing power we carry in our pockets today.
Practical Next Steps for Using √37
If you're working on a project that involves this number, don't just settle for the first few decimals. Here’s how to handle it like a pro:
- For Geometric Accuracy: Always use the Pythagorean theorem $a^2 + b^2 = c^2$ and keep the result in radical form ($\sqrt{37}$) until the very last step of your design.
- For Coding: Use the
math.sqrt(37)function in Python orMath.sqrt(37)in JavaScript rather than hardcoding the decimal 6.082. This ensures your program maintains maximum floating-point precision. - For Education: If you're teaching this, use the proximity of 37 to 36 to explain the concept of "linear approximation." It’s the easiest way to show how we can estimate complex values using simple benchmarks.
The square root of 37 isn't just a digit on a page. It's a bridge between the simple world of integers and the infinite complexity of the real number line. Whether you're a student trying to pass a test or a developer building the next big app, understanding how to navigate these "messy" numbers is a vital skill.