Let’s be honest. Nobody actually wants to calculate standard deviation by hand. Unless you’re a math teacher trying to prove a point or a student stuck in a proctored exam without a decent TI-84, doing the math manually is a special kind of torture. It's tedious. One tiny slip-up—forgetting to square a difference or messing up the mean—and your entire result is garbage. That’s why you’re here. You need to find standard deviation calculator options that are fast, accurate, and maybe even explain what the heck the numbers mean.
Data is messy. Whether you’re looking at stock market volatility, testing the consistency of a manufacturing line, or just trying to figure out if your fantasy football team is reliably mediocre or wildly unpredictable, standard deviation is the metric that matters. It tells you the "spread." Are your data points huddled together like penguins in a storm, or are they scattered across the map?
The Quick Search: Where to Look First
Finding a reliable tool is easy if you know where to look, but annoying if you get stuck in a loop of ad-heavy sites. Most people start with Google’s built-in tools. If you type your data directly into a search bar, Google sometimes tries to help, but it’s hit or miss for complex datasets.
For something more robust, WolframAlpha is the gold standard. It doesn't just give you a number; it gives you the variance, the interquartile range, and a beautiful histogram. It’s the "smart" way to handle it. Then you have the workhorses like Calculator.net or Symbolab. These are great because they usually show the step-by-step breakdown. Seeing the work is huge if you’re trying to learn the process rather than just getting the answer for a report.
Why the Formula Still Matters (Even if You Use a Tool)
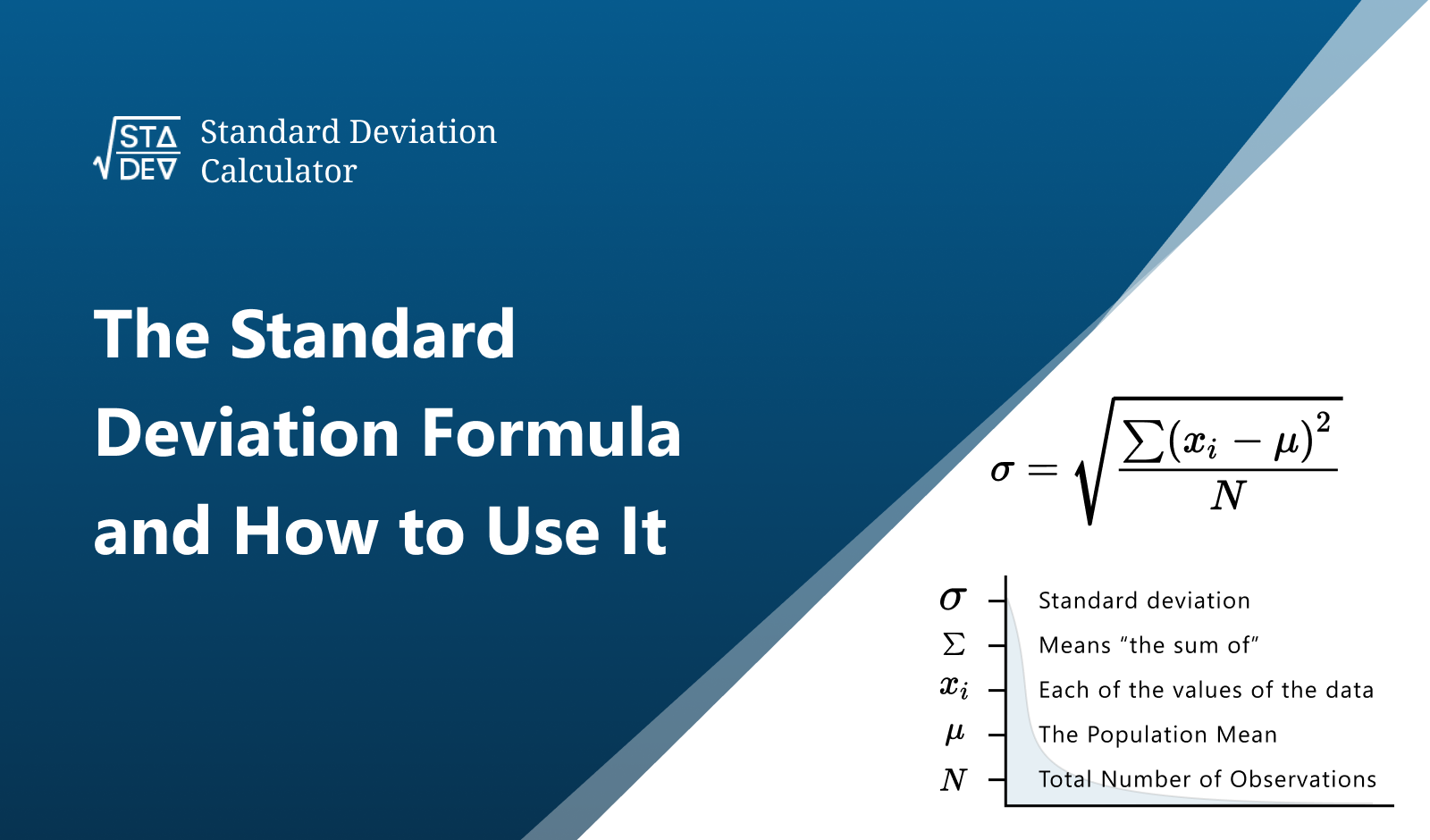
You might think you can just ignore the math since the computer does it for you. Bad idea. You still need to know if you're looking for population standard deviation ($\sigma$) or sample standard deviation ($s$).
👉 See also: AI Image Editing Tool: Why Most Pros Are Using It Wrong
This is where people mess up.
If you have every single data point in existence for a group—say, the heights of every player on one specific basketball team—you use the population formula. You divide by $N$. But if you’re taking a small slice of a larger pie to make an educated guess about the whole thing, you’re dealing with a sample. In that case, you divide by $n-1$. This is known as Bessel's correction. It’s a small tweak that accounts for the fact that samples are usually less diverse than the whole population. If your calculator doesn't ask you which one you want, it might be giving you the wrong answer for your specific context.
Basically, $s = \sqrt{\frac{\sum (x_i - \bar{x})^2}{n - 1}}$.
It looks scary. It isn't. It's just a series of subtractions, squares, and a final square root. But again, that's why we use technology.
Spreadsheets: The Hidden Calculator in Your Pocket
You probably already have a world-class standard deviation tool on your laptop. Excel and Google Sheets are built for this.
If you’re using Excel, you don't need to "find" a calculator online. You just need the formula =STDEV.S(A1:A10) for a sample or =STDEV.P(A1:A10) for a population. I’ve seen people spend twenty minutes copy-pasting data into a random website when they could have just typed a five-second formula into the sheet they already had open. It’s faster. It’s cleaner. Plus, if you change one number in your list, the standard deviation updates instantly.
Real-World Stakes: It's Not Just Math
Why do we care?
Consider pharmaceutical manufacturing. If a company is making 500mg ibuprofen tablets, the standard deviation of the actual dosage needs to be incredibly low. If the "mean" is 500mg but the standard deviation is 50mg, you’ve got a massive problem. Some people are getting 400mg (ineffective) and others are getting 600mg (potentially dangerous).
In finance, standard deviation is synonymous with risk. A mutual fund with a high standard deviation is a roller coaster. It might have a high average return, but the "spread" means you could lose your shirt next Tuesday. Low standard deviation means stability. Boring? Maybe. But safe.
Common Pitfalls When Using Online Tools
Don't just trust the first result you see. Some cheap calculators don't handle "outliers" well, or they might have weird rounding errors that compound.
- Check for Data Limits: Some free web tools capped at 50 or 100 entries. If you have a CSV with 10,000 rows, your browser will probably crash.
- Watch the Delimiters: Does the tool want commas, spaces, or new lines? If you paste a column of numbers and it expects commas, it might treat the whole thing as one giant, nonsensical number.
- The "Zero" Problem: Does the tool count empty cells as zero? This is a classic way to ruin your data. A zero is a data point; a blank is a missing value. They are not the same.
Beyond the Basics: Standard Error and Variance
Once you find standard deviation calculator results that make sense, you’ll probably see other terms pop up. Variance is just the square of the standard deviation. It’s useful for certain statistical tests, but it’s hard to visualize because the units are squared (like "squared dollars" or "squared inches," which makes no sense to the human brain).
Standard Error (SE) is different. It measures how far the sample mean of the data is likely to be from the true population mean. If you're doing serious academic research or A/B testing for a website, you'll be looking at SE more than the raw standard deviation.
Taking Action: How to Choose Your Tool
Stop overthinking it.
If you have a list of 10 numbers for a homework assignment, use an online calculator like MathIsFun or Social Science Statistics. They are simple and don't require a degree to navigate.
If you are analyzing business data, stay in Excel or Power BI. Don't export your sensitive data to a random website just to find a spread. Keep it in-house.
If you are a developer, don't build your own math library. Use NumPy for Python or Math.js for JavaScript. These libraries have been vetted by millions of users and handle the edge cases—like empty sets or non-numeric strings—way better than a custom script would.
📖 Related: Wait, Is My Phone Bricked? What Brick Mean in the Tech World
To get started right now, gather your data and decide: am I looking at the whole group or just a slice? Once you know that, pick your platform and run the numbers. The real value isn't in the calculation itself; it's in what you do with the information once you see how spread out your reality actually is. If your standard deviation is higher than you expected, it’s time to look at your processes and figure out why things are so inconsistent.
Practical Next Steps
- Identify your data type: Determine if you have "Population" data (the whole set) or "Sample" data (a portion). This dictates whether you use the $N$ or $n-1$ version of the formula.
- Select your environment: For quick one-off tasks, use an online tool like WolframAlpha. For recurring business data, use the
=STDEV.Sfunction in Google Sheets. - Clean your input: Ensure there are no "hidden" characters or text strings in your data set that could cause the calculator to return an error or an incorrect mean.
- Analyze the "Why": If your standard deviation is high, look for outliers—individual data points that are drastically different from the rest—and decide if they are errors or genuine anomalies.